What Is End-To-End Encryption And How Does It Work?

Table of Contents
End-to-end encryption, often shortened to E2EE, is a way of securing your communication so that only you and the person you're talking to can read what's sent. It scrambles your data right on your device and can only be unscrambled by the intended recipient's device. Think of it this way: no one in the middle—not your internet provider, not the app's own servers, not even a determined hacker—can decipher your message. It’s the gold standard for digital privacy.
Ready To Fax?
Start sending faxes online in seconds with FaxZen - No account required
Send Fax Now 🚀Ready to protect your sensitive documents? Discover how FaxZen uses top-tier security to keep your information safe. Explore our secure online faxing solution and send your first fax with confidence today.
Your Guide To Understanding End-To-End Encryption

Imagine sending a secret message in a locked box. You lock it, send it off, and only the person you sent it to has the one unique key that can open it. The mail carrier can't peek inside, and neither can anyone else who handles it along the way. That's exactly how end-to-end encryption works for your digital files and messages. This powerful security method has become non-negotiable for protecting everything from quick personal chats to critical business documents. In a world where data breaches feel like a daily headline, E2EE provides a crucial defense, making sure your private information stays private from the moment you hit "send" until it lands safely with your recipient.
The philosophy behind E2EE is beautifully simple: privacy by design. While other types of security might only protect your data while it's in transit, E2EE secures it for the entire journey. That distinction is what makes all the difference. For instance, when sharing sensitive files online, you need to know they’re protected at every single step. This is a core principle behind true secure document sharing. You can also see a great breakdown of the importance of end-to-end encryption in video conferencing to understand how critical it is in other real-time applications. This guide will break down how E2EE works in simple terms, show you where it's used every day, and explain why you should look for it in the digital services you rely on.
How E2EE Creates Your Digital Secret Handshake

At its core, end-to-end encryption works like a high-tech digital mailbox system. The real magic behind this security method is something called asymmetric cryptography, which relies on a matched pair of mathematically linked keys: one public key and one private key. Think of your public key as the mail slot on a personal, super-secure mailbox. Anyone can find it and use it to drop a letter inside for you. But once that message slides through the slot, it's locked down tight. The only way to open that mailbox and read what's inside is with your unique private key. This key is yours and yours alone—it never leaves your device and is kept completely secret. When someone sends you an encrypted message, their device uses your public key to scramble it into unreadable code. From that point forward, only your private key can turn that gibberish back into a legible message.
So, how do two devices even start this secure conversation? It all begins with a process often called a key exchange, or a "digital handshake." When you initiate a new chat, your devices automatically and invisibly swap public keys. This initial handshake establishes a secure channel just long enough to create a unique, temporary key—known as a session key—that is shared only between the two of you for that specific conversation. This session key then encrypts every message that follows, keeping the entire exchange private. This rock-solid framework ensures that even if a third party intercepts your data, all they'll see is a meaningless jumble of characters. This very principle was at the heart of the debate after the 2015 San Bernardino shooting, when the FBI demanded Apple create a "backdoor" to unlock an E2EE-protected iPhone. Apple refused, arguing that weakening encryption for one phone would compromise the security of millions of users, igniting a global conversation about law enforcement's struggle to access encrypted data, a challenge they've dubbed "going dark."
What's the Difference Between Public and Private Keys?
Understanding how these two keys work together is the key to seeing why end-to-end encryption is the gold standard for digital privacy.
| Key Type | Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Public Key | Encrypts data being sent to you. It's meant to be shared openly. | The mail slot on your secure mailbox. |
| Private Key | Decrypts the data you receive. It must be kept secret on your device. | The physical key that unlocks your mailbox. |
E2EE vs. Encryption In Transit: What's The Difference?
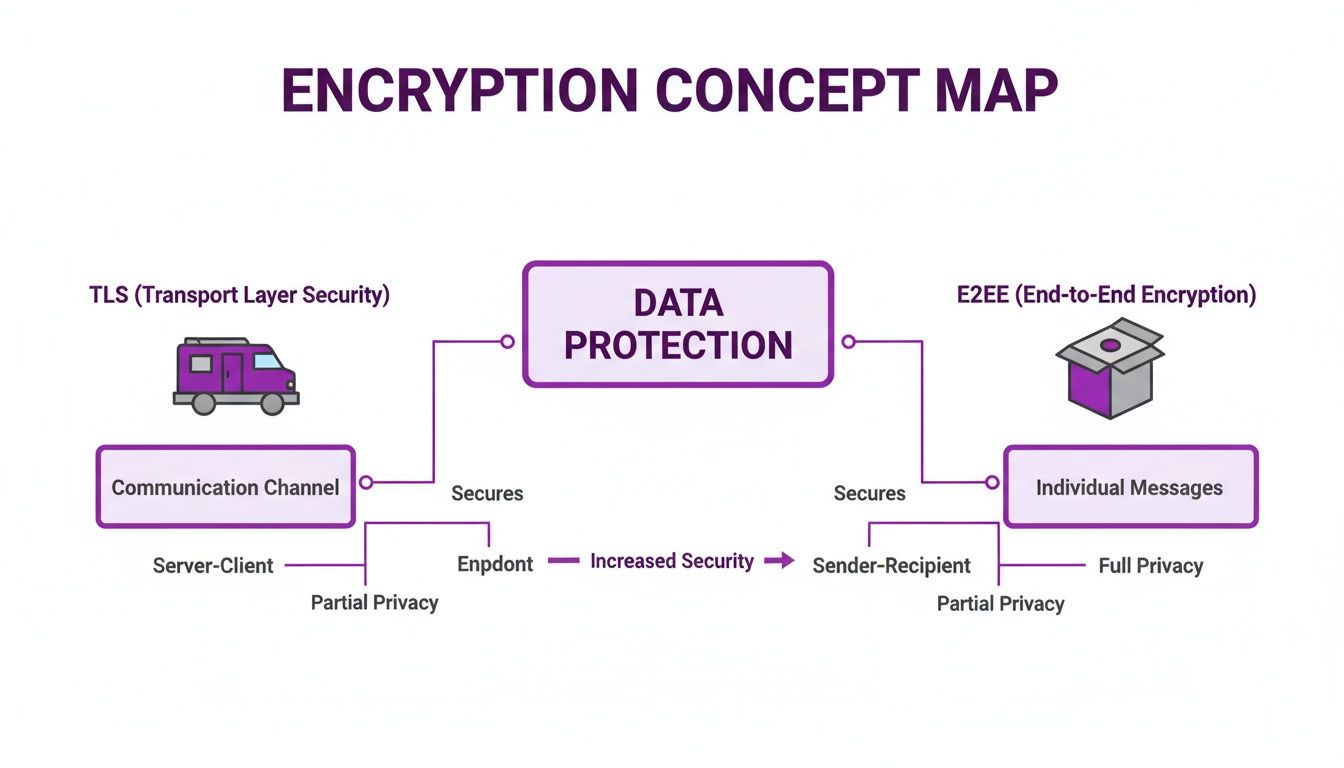
Not all encryption is created equal. Many services use encryption in transit, or Transport Layer Security (TLS). This is the technology that gives you the padlock icon in your browser's address bar. Think of TLS as an armored truck protecting your message while it travels to the service provider's server. The problem? When the truck arrives, the company has the key. They unlock it to process or store your message, leaving your data vulnerable on their server. End-to-end encryption is different. It puts your message in a sealed, impenetrable box for its entire journey. The service provider is just the mail carrier; they can move the box, but they have absolutely no way to see what's inside.
The biggest difference comes down to who can access your data. With encryption in transit, there's a "middleman"—the service provider—who can theoretically access your data on their servers. This creates a massive target for hackers. End-to-end encryption completely removes that middleman risk. The provider never gets the keys to your data, so their servers only ever handle scrambled, unreadable information. This is often called a "zero-knowledge" system, which means even if their servers were breached, your messages would remain gibberish to the attackers. For the highest level of privacy, such as when you can you securely fax from a cell phone, E2EE is the clear winner because it removes the service provider as a potential weak point.
Where You Encounter E2EE In Your Daily Life

You probably use end-to-end encryption every single day without even realizing it. It’s the invisible shield working behind the scenes in many of the apps you already trust. The most common place you'll find E2EE is in your messaging apps. Services like Signal, WhatsApp, and Apple's iMessage have made it a default feature, securing billions of conversations around the globe. This ensures that your private chats, photos, and video calls stay completely private.
But E2EE isn't just for texting. Its "zero-knowledge" privacy principle has become the gold standard for a whole range of digital tools. Modern online services that handle sensitive files, such as a platform for HIPAA compliant online fax, use E2EE to safeguard everything from client contracts to financial records during transmission.
| Service Category | Examples with E2EE by Default |
|---|---|
| Messaging Apps | WhatsApp, Signal, iMessage |
| Password Management | 1Password, Bitwarden, Dashlane |
| Cloud Storage | Tresorit, Sync.com, pCloud |
| Secure Communications | Secure Online Faxing, ProtonMail |
Debunking Common E2EE Myths And Limitations
End-to-end encryption is powerful, but it’s not a magic shield against every online threat. One of the biggest myths is that E2EE makes you completely anonymous. It doesn’t. E2EE is focused on protecting the privacy of your content, not the anonymity of your identity. Think of E2EE like a sealed, tamper-proof envelope. It protects the letter inside, but the outside of the envelope—with the sender, recipient, and postmark—is still visible. This information is called metadata, and it’s not encrypted. An adversary might not be able to read your message, but they can still learn a surprising amount just by analyzing your metadata.
Another crucial reality check: E2EE’s protection only exists between devices. The security of the whole system is only as strong as the endpoints themselves—your device and the recipient's. If either device is compromised with malware or spyware, a hacker can read messages as you type them or take a screenshot, completely bypassing the encryption. Ultimately, a smart security strategy is about layers. You need more than just an encrypted service; you also have to secure the devices you use. This is a core part of any modern protocol, including fax machine security. E2EE is a vital layer, but it works best when it’s part of a complete defense.
Related Articles
- Understanding the Basics of Secure Document Sharing
- How HIPAA Compliant Online Fax Services Work
- A Guide to Fax Machine Security Vulnerabilities
- Internet Faxing for HIPAA Compliance
Frequently Asked Questions
Is end-to-end encryption actually unbreakable? The math behind it, using algorithms like AES-256, is considered unbreakable with current technology. However, security failures usually happen at the "endpoints." If a device is compromised with malware, an attacker can read messages after they are decrypted, bypassing the encryption entirely.
Does E2EE make me anonymous? No. E2EE protects your content's privacy, not your anonymity. It hides what you’re saying, but not that you’re communicating. Metadata—like who you messaged and when—is often not encrypted and can be seen by service providers.
If my public key is shared, can't someone use it to read my messages? No. The public key only works in one direction: locking (encrypting). It cannot be used for unlocking (decrypting). That power belongs exclusively to your private key.
Why don't all services use E2EE? Many services need to access your data to provide features like content search or targeted advertising. E2EE makes these server-side functions impossible because the service provider cannot read the data.
What happens if I lose my private key? Losing your private key means you've lost the ability to decrypt any messages sent to you. It’s like losing the only key to your mailbox. This is why securely managing your private key is so critical.



